AWI 300 - Materials
3.3 Panel Products
a) The use of??other than those identified within this standard that display unusual characteristics desirable for aesthetic and design reasons shall be as agreed upon between buyer and seller.
b)???direction is indicated by its size?; for example, 1219 mm x 2438 mm [48″ x 96″] means the??direction??with the 2438 mm [96′] direction, whereas a 2438 mm x 1219 mm [96″ x 48″] panel’s grain direction runs with the 1219 mm [48″] dimension.
c)??shall be of manufacturer/supplier’s choice.
3.3.1 Reference Standards
a) The standards referenced below, adopted for the performance, fabrication, and appearance of face veneers, laminates, overlays, backers, and cores, serve as the basis for evaluation of?,?s, and other properties:
| Material | Acronym | Reference Standard |
|---|---|---|
| ? and veneers | ?ANSI/ HP-1 (latest edition) | |
| ? veneers | ?ANSI/HPVA HP-1 (latest edition) | |
| ?Medium Density | ? | ?US Plywood Standard APA PS-1 (latest edition) |
| ? | ?HDO | ?US Plywood Standard APA PS-1 (latest edition) |
| ?Thermally-fused Laminates ( or ) | ?/MCP | ?Composite Panel Association 2009 Voluntary Compendium of Standards for Decorative Overlay |
| ? | ? | ?ISO 4586 (latest edition) |
| ?Vinyl Film | ?Composite Panel Association 2009 Voluntary Compendium of? Standard for decorative | |
| ? | ?ANSI A135.4 (latest edition) | |
| ? | ?PTB | ?ANSI A208.1 (latest edition): M-2 or better. |
| ?Medium Density Fiberboard | ?Medium Density Fiberboard MDF ANSI A208.2 (latest edition) | |
| ? | ?OSB | ?APA PS-2 (latest edition) |
| ? | ?ANSI/HPVA HP-1 (latest edition) |
3.3.2 Cores
a) Core materials shall follow standards referenced in?3.3.1 Table 1. Alternative core materials not listed shall be as agreed upon by buyer and seller.
b) Fire retardant and moisture resistant core shall be color tinted or otherwise documented.
c) Core shall be manufacturer/supplier’s choice within the provisions of this standard.
d) MDO and HDO products shall be of?.
e)?, OSB, or lumber cores are not guaranteed against warping,?, or?.
3.3.3 Surfaces
a) Panel layup shall be for interior use (unless specified otherwise) and shall be constructed with an odd number of plies.
b) Panel layup requires balanced construction of faces, thickness, and??to produce a?-free panel suitable for its intended use.
c) Panel layup shall have a rigid glue line. Delamination or separation is not permitted.
d) Panel layup shall not use??unless otherwise indicated in this standard.
e) Panel layup requires cores of veneer,?, particleboard, MDF, or a combination thereof. Veneer core shall not be used for cabinet door or drawer front components.
f) Surface distortions or defects, such as bubbling,?, cracking, crazing or ridges in the exposed face veneer, shall not occur.
g) Telegraphing shall not exceed .1 mm [.004″] in any 76.2 mm [3″] span.
h) Lamination over existing laminate surfaces is not permitted.
a)??is available in a wide range of surface textures and glosses. This standard does not differentiate between these surface characteristics. It is the responsibility of the design professional to stipulate the surface characteristics of the HPDL to be used.
b) High gloss HPDL will highlight minor core and surface imperfections. Use of high gloss HPDL shall be as agreed to between owner/design professional and?.
a) Veneer shall be of sufficient thickness to prevent exposure of core after sanding or finishing.
b) Edges of multi-?faces shall appear parallel.
c) Backing species shall be manufacturer/supplier’s choice.
d) Figure is independent of species and aesthetic grade. Special requirements shall be so specified.
e) Rift grain oak may have up to twenty-five percent of the exposed area containing medullary??(often referred to as fleck).
f) Core shall be manufacturer/supplier’s choice, within the provisions of this standard.
a) Where required within the AWI Standards, shall include:
| Face Material | Balance Material | Thickness |
|---|---|---|
| ?HPDL | Compatible with face material | Same as face material |
| ?TFL | Compatible with face material | Same as face material |
| Wood veneer | ?with face veneer | Same as face veneer |
b) Or any independently-tested (See AWI’s Balance Material Test Methodologies) material that maintains panel flatness and meets
a) Where required within AWI Standards, may include the following:
b) Laminate conforming to ISO 4586 (latest edition) .5 mm [.020″] min. thickness.
c) Man-made wood fiber veneers, impregnated with acrylic melamine, fortified, high load resin system, .5 mm [.020”] min thickness.
d) Synthetic polymer-treated backing sheet designed for use with HPDL .43 mm – .48 mm [.017″ – .019″]??thickness.
e) Thermoset resin-treated wood fiber, 3-?construction, .5 mm [.020″] min. thickness.
f) Phenolic resin impregnated kraft paper .4 mm [.016″] nominal thickness.
g) Polyester or melamine overlay.
3.3.4 Other Materials
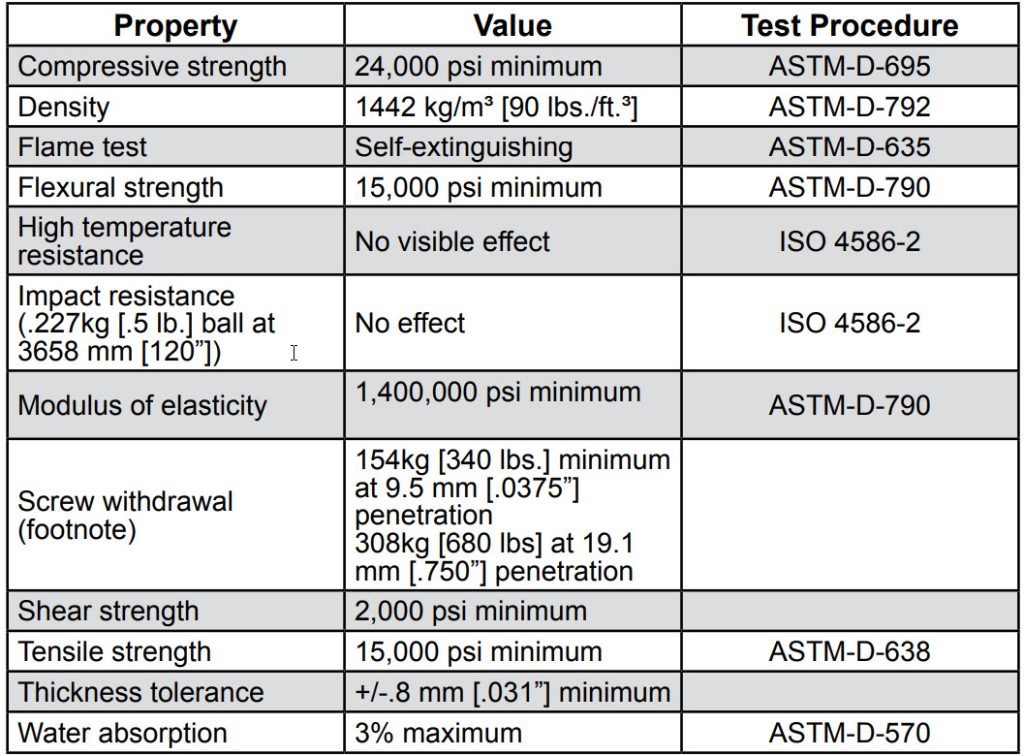
a) Epoxy resin shall be a panel produced from a composite of epoxy resin, silica, inert fillers, and organic hardeners cast and cured in ovens at elevated temperatures, homogeneous throughout, and nonabsorbent.
b) Epoxy resin shall conform to the following minimum performance properties:
a) stone shall not be subject to minimum performance properties established by this standard because it is a natural product.
a) Engineered stone shall be subject to the manufacturer/supplier’s documented instructions
a) shall be subject to the manufacturer/supplier’s documented instructions.
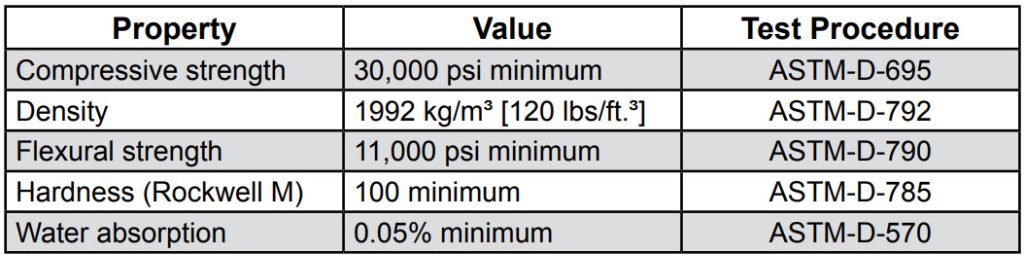
a)??shall be composed of melamine-impregnated decorative surface papers superimposed over a varying number of kraft phenolic core sheets to achieve a desired thickness.
b) Solid phenolic shall conform to the following minimum performance properties: